variable head permeability test procedure|falling head vs constant permeability : OEM Variable-head permeability tests can be performed in open boreholes or monitoring wells having either a long screen or several screened zones. In all cases, a test .
webHot Honey 22 Slot Machine. For a video slot with an adult theme, check out Hot Honey 22 from MrSlotty where you can enjoy the sight of some seriously sexy girls gracing the reels. If you like the look of women with ink this game is for you as you’ll be treated to glimpses of bare flesh as you play the reels for cash.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Atacante policial, 'quarentão' e com 'desprezo' por Haaland: como é a seleção que levou 14 da França e hoje desafia Holanda. Gibraltar x Holanda, válido pelas Eliminatórias da .
Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow .In the laboratory we employ two methods. One is constant head permeability test. And another one is Falling head or variable head permeability test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed .Figure 12.7 Variable head tests in boreholes, (a) Falling head test. Water is added to the borehole to raise water levels, inducing flow from the borehole into the surrounding strata, (b) Rising head test.
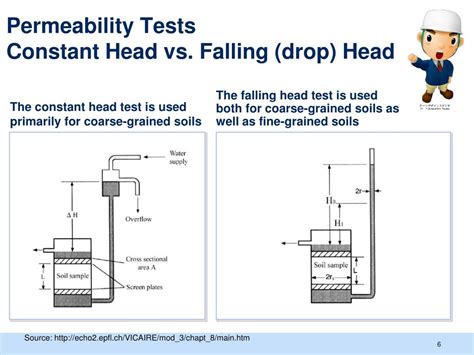
This test helps measure the permeability of soil, especially for less compacted types. The permeability impacts various aspects, such as settlement rates under loads, the design of .
А2.2 VARIABLE HEAD (FALLING HEAD) TEST - TEST PROCEDURE. Each test is carried out at a specific depth interval known as the ‘test section’ (Figure A2.1). The whole test section must be below the groundwater level. The initial . Variable-head permeability tests can be performed in open boreholes or monitoring wells having either a long screen or several screened zones. In all cases, a test .
This video shows how to perform a falling head permeability test for fine-grained soil.
The falling head permeability test, also called the variable head test, is a common way to test the permeability of relatively fine soil in a laboratory. The variable head permeameter is utilized to compute the permeability of comparatively less porous soils. The coefficient of permeability is expressed by: Where, = .It is a valid test for soils with a high rate of flow like sands and gravels, but also some clay soils. Falling Head Test allows the head to decrease as water infiltrates the sample, diminishing the pressure over the course of the test. .
Procedure: The specimen is connected to a stand-pipe, and the time for water level drop from initial to final head is recorded. This is repeated until three successive observations show similar time intervals. . In conclusion, the Variable Head Permeability Test is a comprehensive procedure that involves careful preparation, precise . This video explains the procedure of constant head test to determine the soil permeability. This test is performed on coarse-grained soil with a high coeffic.1.1 This test method covers the determination of the coef-ficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of perme-ability of .
Where, K27 = Permeability at 27°C KT = Permeability at T°C μ27 = Coefficient of Viscosity at 27°C μT = Coefficient of Viscosity at T°C. 5.5 Presentation of Results: The values of permeability at T 0 C and 27 0 C are reported. Also reported are corresponding void ration, degree of saturation and water content. 6. Falling Head Test Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to interpret such tests. This method, also called the Variable Head Permeability test, is suitable for fine grain soils with intermediate-low permeability such as clays and silts. Figure 2 shows a schematic representation of the test which basically works the same as the constant head permeability test, the only difference being that the water head will not be constant .
Permeability (hydraulic conductivity) can be determined by undertaking in-situ tests in boreholes or standpipe piezometers. The test method involves variable head (rising or falling) or constant head procedures and requires knowledge of the groundwater level. The type of test undertaken depends on the soil type.IIT Gandhinagar, Soil Mechanics Lab Page 1 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY GANDHINAGAR Department of Civil Engineering Soil Mechanics Laboratory
NOTE 7 BS EN ISO 22282-2 specifies requirements for the determination of the local permeability in soils and rocks below and above groundwater level in an open hole by water permeability. Constant flow rate test method is suitable for k-value greater than 10 –6 m/s; the variable head test method is suitable for k-value between 10 –6 m/s and .HC, also known as the coefficient of permeability, of the specimens was evaluated through a falling-head method, compat- ible with ASTM D5084 Method C [ASTM D5084 (ASTM 2016)] for porous materials.6.4 Presentation of Results : The permeability values are reported at T0C and 270C. The state of sample is also reported in terms of water content, void ration and degree of saturation. 7. Video Constant Head Permeability Test Falling Head Permeability Test 8. Download Download PDFThe falling head permeability test (variable head test) is a common laboratory testing method performed to determine the permeability of fine grained soils with medium and low permeability such as silts and clays. In this test a relatively short sample is connected to a standpipe which . Test procedure: 1. Determine the standpipe area (a .
The falling head permeability test, also called the variable head test, is a common way to test the permeability of relatively fine soil in a laboratory. In .This standard operating procedure (SOP) outlines the procedure for the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for granular soils. 2.0 METHOD SUMMARY This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils.So the falling head test suits lower permeability samples by reaching measurable equilibration rates faster but requires dynamic gradient corrections in determining permeability unlike the constant rate of the fixed head .
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of permeability of granular soils that may occur in natural deposits as placed in embankments, or when used as base courses under pavements.FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is defined For determination of the permeability of a soil specimen by the variable head permeameter. Theory. The variable head permeameter is utilized to compute the permeability of comparatively less porous soils. The coefficient of permeability is expressed by: Where, = initial head, = final head, t= time interval, a= cross-sectional area of the liquid .
The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: 1. 4.5 These test methods provide a means for determining hydraulic conductivity at a controlled level of effective stress. Hydraulic conductivity varies with varying void ratio, which changes when the effective stress changes. If the void ratio is changed, the hydraulic conductivity of the test specimen will likely change, see Appendix X2.To determine the relationship .
Variable head permeability test, leaka ge errors. 1. Project Engineering Manager, ARCHIRODON NV, . The procedure is based on the theory, developed by Hantush and Jacob, of the nonsteady flow .tion of coefficient of permeability of soils using falling head and the constant head methods. This test is recommended for soils with coefficient of permeability in the range lo- 3 to 10-v cm/s and maximum particle size of 9.5 mm. 2. TERMINOLOGY 2.1 For the purpose of this standard, definition terms given inTest Procedure. 1.For the constant head arrangement, the specimen shall be connected through the top inlet to the constant head reservoir. . Constant head permeability test is suitable for cohesionless soils. For cohesive soils falling head method is suitable. Computation. Coefficient of permeability for a constant head test is given by .Soil Lab Boss Dave Anderson demonstrates how a falling head permeability test is performed using a triaxial shear testing apparatus.
Constant head method – suitable for coarse grained soils. ii. Variable head method-suitable for fine grained soils. PERMEABILITY TEST – VARIABLE HEAD METHOD IS : 2720 (Part 17) - 1986. Aim: To determine the co-efficient of permeability of the given soil sample at desired density. by variable head method. Furthermore, the gathering of results during the performance of the constant head permeability test is briefer than the one of the adapted falling head permeability test, since the latter requires the saturation of the samples, which takes at least 7 days. •
falling head vs constant permeability
falling head tests in borehole
falling head soil permeability apparatus
Mais Noticias - Portilho Online – Sem Censura ! – Noticias d.
variable head permeability test procedure|falling head vs constant permeability